AVL树
一、前言
AVL树历史,在计算机科学中,AVL 树以其两位苏联发明家Georgy Adelson-Velsky和 Evgenii Landis的名字命名,他们在 1962 年的论文“信息组织算法”中发表了它。它是一种自平衡二叉搜索树(BST),这是发明的第一个这样的数据结构。
二、AVL树数据结构
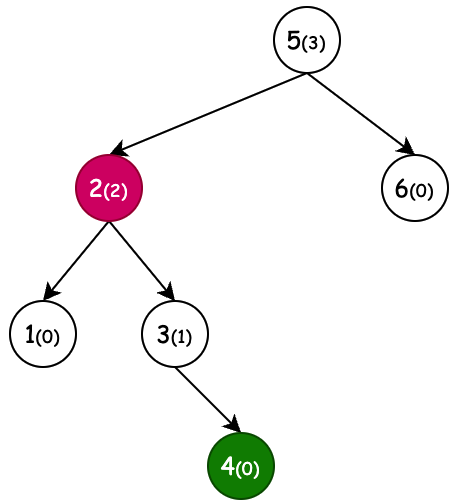
AVL 自平衡二叉树的出现,其目的在于解决二叉搜索树退化成链表的问题。当我们向BST二叉搜索树顺序存入1、2、3、4、5、6、7个元素时,它会退化成一条链表,因而失去树查询的时间复杂度,所以我们需要AVL树平衡树高。如图所示

那么AVL树是怎么平衡树高的呢?当二叉树的左右分支树高差不为1时,需要进行左旋或者右旋,来调衡树高。这有点像开车的时候,如果车头偏左就往右打方向盘,车头偏右就往左打方向盘是一个道理。那这个方向盘(左旋、右旋)是怎么打的呢,主要分以下四种情况;
| 左旋(新增节点6) | 右旋(新增节点1) | 左旋+右旋(新增节点4) | 右旋+左旋(新增节点3) |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 条件 :节点4,平衡因子为-2,左旋 | 条件 :节点3,平衡因子为2,右旋 | 条件 :节点3,平衡因子为2,右旋。但当节点2平衡因子-1先左旋。 | 条件 :节点2,平衡因子为-2,左旋。但当节点5平衡因子1先右旋。 |
- 节点树高:以节点4为说明,最长的左右分支节点个数,就是节点4的最大树高。这里节点4左右孩子节点最长路径都为2,所以它的树高为2。同理可计算其他节点树高。
- 平衡因子:通过当前节点的左右子节点作差计算平衡因子,之后AVL树通过平衡因子,定义了什么时候进行左旋和右旋。
三、AVL树代码实现
对于 AVL 树的实现与 BST 二叉搜索树相比,在树的节点定义上多了一个树高的属性。也有些AVL树使用的是平衡因子的属性,就是通过树高计算后的结果。树节点代码结构如下:
package xp.day2;
public class Node<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
public K key;
public V value;
// AVL 树所需属性
public int height;
public Node<K, V> parent;
public Node<K, V> left;
public Node<K, V> right;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
接下来就分别通过代码讲解下一颗AVL树的左旋、右旋、左旋+右旋、右旋+左旋的代码操作。不要担心这没有多复杂,只要你能搞清楚左旋,就能搞清楚右旋。两旋弄懂组合就没啥难度了。
1. 左旋

对x进行左旋,意味着"将x变成一个左节点"。左旋的伪代码《算法导论》:
LEFT-ROTATE(T, x)
01 y ← right[x] // 前提:这里假设x的右孩子为y。下面开始正式操作
02 right[x] ← left[y] // 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”,即 将β设为x的右孩子
03 p[left[y]] ← x // 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子的父亲”,即 将β的父亲设为x
04 p[y] ← p[x] // 将 “x的父亲” 设为 “y的父亲”
05 if p[x] = nil[T]
06 then root[T] ← y // 情况1:如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将y设为根节点
07 else if x = left[p[x]]
08 then left[p[x]] ← y // 情况2:如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
09 else right[p[x]] ← y // 情况3:(x是它父节点的右孩子) 将y设为“x的父节点的右孩子”
10 left[y] ← x // 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
11 p[x] ← y // 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
左旋的java代码实现:
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* px px
* / /
* x y
* / \ --(左旋)-. / \
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
*
*/
private void rotateLeft(TreeNode<T> x) {
// 设置x的右孩子为y
TreeNode<T> y = x.right;
// 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”
// 如果y的左孩子不为空的话,将 “y的左孩子的父亲” 设为 “x”
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
// 将"y的父亲" 从 "x" 修改为 "x的父亲"
y.parent = x.parent;
// 如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将 y 设为根节点
if (x.parent == null) {
this.root = y;
} else {
// 如果 x 是它父节点的左孩子,则将 y 设为 “x的父节点的左孩子”
if (x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y;
}
// 如果 x 是它父节点的左孩子,则将 y 设为 “x的父节点的左孩子”
if (x.parent.right == x) {
x.parent.right = y;
}
}
// 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
y.left = x;
// 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
x.parent = y;
}
2. 右旋
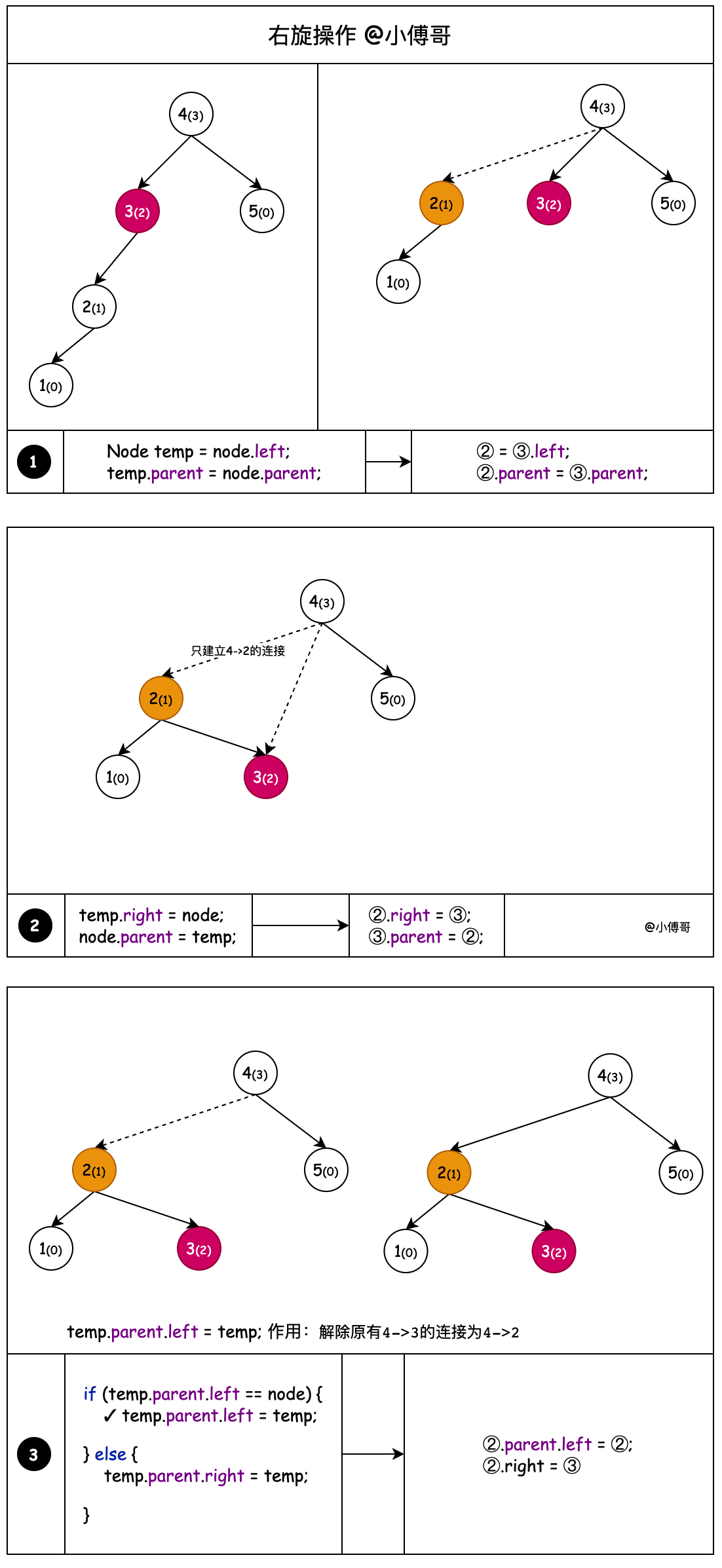
对x进行右旋,意味着"将x变成一个右节点"。右旋的伪代码《算法导论》:
RIGHT-ROTATE(T, y)
01 x ← left[y] // 前提:这里假设y的左孩子为x。下面开始正式操作
02 left[y] ← right[x] // 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”,即 将β设为y的左孩子
03 p[right[x]] ← y // 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”,即 将β的父亲设为y
04 p[x] ← p[y] // 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲”
05 if p[y] = nil[T]
06 then root[T] ← x // 情况1:如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
07 else if y = right[p[y]]
08 then right[p[y]] ← x // 情况2:如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的左孩子”
09 else left[p[y]] ← x // 情况3:(y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“y的父节点的左孩子”
10 right[x] ← y // 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
11 p[y] ← x // 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
右旋的java代码实现:
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(y)进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行右旋):
* py py
* / /
* y x
* / \ --(右旋)-. / \
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \
* lx rx rx ry
*
*/
private void rotateRight(TreeNode<T> y) {
// 设置x是当前节点的左孩子。
TreeNode<T> x = y.left;
// 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”
// 如果"x的右孩子"不为空的话,将 “x的右孩子的父亲” 设为 “y”
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right != null) {
x.right.parent = y;
}
// 将 “x的父亲” 从 "y" 修改为 “y的父亲”
x.parent = y.parent;
// 如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
if (y.parent == null) {
this.root = x;
} else {
// 如果 y 是它父节点的右孩子,则将 x 设为“y的父节点的右孩子”
if (y == y.parent.right) {
y.parent.right = x;
}
// 如果 y 是它父节点的左孩子,将x设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
if (y == y.parent.left) {
y.parent.left = x;
}
}
// 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
x.right = y;
// 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
y.parent = x;
}
3. 再平衡
avl树的再平衡是在插入树中插入或者删除节点后,根据插入节点或者被删除节点开始往父亲节点递归检查树高的平衡因子,并根据平衡因子的不同进行相应的调节,是树维持平衡特性。
java实现代码如下:
private void rebalance(Node<K, V> node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
refreshHeight(node);
Node<K, V> parent = node.parent;
int factor = factor(node);
switch (factor) {
case 2: // 左子树比右子树高,需要平衡
// 左子树的左子树比左子树的右子树要高,属于右旋
if (factor(node.left) >= 0) {
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node;
rotateRight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
} else {
// 左子树的右子树比左子树的左子树要高,属于先左旋再右旋
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node.left;
rotateLeft(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode.parent);
rotateNode = node;
rotateRight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
}
break;
case -2: // 右子树比左子树高
// 右子树的右子树比右子树的左子树要高,需要左旋
if (factor(node.right) <= 0) {
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node;
rotateLeft(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
} else {
// 右子树的左子树比右子树要高,需要先右旋再左旋
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node.right;
rotateRight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode.parent);
rotateNode = node;
rotateLeft(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
rebalance(parent);
}
private void refreshHeight(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
int leftHeight = (node.left == null) ? -1 : (node.left).height;
int rightHeight = (node.right == null) ? -1 : (node.right).height;
node.height = 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
private int factor(Node node) {
int leftHeight = (node.left == null) ? -1 : (node.left).height;
int rightHeight = (node.right == null) ? -1 : (node.right).height;
return leftHeight - rightHeight;
}
四、AVL树完整代码
package xp.day2;
import com.utils.BinaryTreeInfo;
public class AVLTree<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
public Node<K, V> root;
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* px px
* / /
* x y
* / \ --(左旋)-. / \
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
*
*/
private void rotateLeft(Node<K, V> x) {
// 设置x的右孩子为y
Node<K, V> y = x.right;
// 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”
// 如果y的左孩子不为空的话,将 “y的左孩子的父亲” 设为 “x”
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
// 将"y的父亲" 从 "x" 修改为 "x的父亲"
y.parent = x.parent;
// 如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将 y 设为根节点
if (x.parent == null) {
this.root = y;
} else {
// 如果 x 是它父节点的左孩子,则将 y 设为 “x的父节点的左孩子”
if (x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y;
}
// 如果 x 是它父节点的左孩子,则将 y 设为 “x的父节点的左孩子”
if (x.parent.right == x) {
x.parent.right = y;
}
}
// 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
y.left = x;
// 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
x.parent = y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(y)进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行右旋):
* py py
* / /
* y x
* / \ --(右旋)-. / \
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \
* lx rx rx ry
*
*/
private void rotateRight(Node<K, V> y) {
// 设置x是当前节点的左孩子。
Node<K, V> x = y.left;
// 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”
// 如果"x的右孩子"不为空的话,将 “x的右孩子的父亲” 设为 “y”
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right != null) {
x.right.parent = y;
}
// 将 “x的父亲” 从 "y" 修改为 “y的父亲”
x.parent = y.parent;
// 如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
if (y.parent == null) {
this.root = x;
} else {
// 如果 y 是它父节点的右孩子,则将 x 设为“y的父节点的右孩子”
if (y == y.parent.right) {
y.parent.right = x;
}
// 如果 y 是它父节点的左孩子,将x设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
if (y == y.parent.left) {
y.parent.left = x;
}
}
// 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
x.right = y;
// 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
y.parent = x;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
insert(key, value);
}
public void insert(K key, V value) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(key, value);
return;
}
Node<K, V> parent = root;
Node<K, V> search = root;
while (search != null) {
parent = search;
if (key.compareTo(search.key) == 0) {
search.value = value;
return;
}
search = key.compareTo(search.key) < 0 ? search.left : search.right;
}
Node<K, V> node = new Node(key, value);
if (key.compareTo(parent.key) < 0) {
parent.left = node;
} else {
parent.right = node;
}
node.parent = parent;
rebalance(node);
}
public V get(K key) {
Node<K, V> Node = search(key);
return Node == null ? null : Node.value;
}
public Node<K, V> search(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
Node<K, V> search = root;
while (search != null) {
if (key.compareTo(search.key) == 0) {
return search;
}
search = key.compareTo(search.key) < 0 ? search.left : search.right;
}
return null;
}
public void remove(K key) {
Node<K, V> search = search(key);
if (search == null) {
return;
}
delete(search);
}
public void delete(Node<K, V> node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
if (node == root) {
root = null;
return;
}
if (node == node.parent.left) {
node.parent.left = null;
}
if (node == node.parent.right) {
node.parent.right = null;
}
Node<K, V> parent = node.parent;
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
node.parent = null;
rebalance(parent);
return;
}
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
Node<K, V> successor = node.right;
while (successor.left != null) {
successor = successor.left;
}
node.key = successor.key;
node.value = successor.value;
delete(successor);
return;
}
Node<K, V> replace = node.left == null ? node.right : node.left;
transplant(node, replace);
rebalance(replace);
}
protected void transplant(Node node, Node replace) {
if (node == root) {
root = replace;
} else if (node.parent.left == node) {
node.parent.left = replace;
} else {
node.parent.right = replace;
}
// 设置父节点
if (replace != null) {
replace.parent = node.parent;
}
}
private void rebalance(Node<K, V> node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
refreshHeight(node);
Node<K, V> parent = node.parent;
int factor = factor(node);
switch (factor) {
case 2: // 左子树比右子树高,需要平衡
// 左子树的左子树比左子树的右子树要高,属于右旋
if (factor(node.left) >= 0) {
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node;
rotateRight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
} else {
// 左子树的右子树比左子树的左子树要高,属于先左旋再右旋
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node.left;
rotateLeft(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode.parent);
rotateNode = node;
rotateRight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
}
break;
case -2: // 右子树比左子树高
// 右子树的右子树比右子树的左子树要高,需要左旋
if (factor(node.right) <= 0) {
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node;
rotateLeft(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
} else {
// 右子树的左子树比右子树要高,需要先右旋再左旋
Node<K, V> rotateNode = node.right;
rotateRight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode.parent);
rotateNode = node;
rotateLeft(rotateNode);
refreshHeight(rotateNode);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
rebalance(parent);
}
private void refreshHeight(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
int leftHeight = (node.left == null) ? -1 : (node.left).height;
int rightHeight = (node.right == null) ? -1 : (node.right).height;
node.height = 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
private int factor(Node node) {
int leftHeight = (node.left == null) ? -1 : (node.left).height;
int rightHeight = (node.right == null) ? -1 : (node.right).height;
return leftHeight - rightHeight;
}
}
五、常见面试题
- AVL 树平衡因子怎么计算?
- AVL 树左旋操作的目的是什么?
- AVL 树左旋操作的流程是什么?
- AVL 树什么情况下要左旋+右旋?
- AVL 树的插入和读取的时间复杂度?